Have you ever had a computer program ask you the following question: "In what format do you want to save the image? And, underneath, a long list of extensions, the .jpg, the .png and another alphabet soup. And then you ended up choosing any of them, or choosing JPG because it was the lightest.
But these image formats don't exist just to confuse you. Each of them has its advantages and disadvantages, and in some situations it can be important to know which one you should use. That's why we've made this short list to help you understand the differences that exist between the main image file formats, and which one you should use for each occasion. Check it out:
1. BMP
BMP is an abbreviation for "bitmap" or bitmap. This name is almost literal, because an image in .bmp format is basically a file that describes how many pixels the image has and what the color of each pixel is. To do this, the file includes, for each pixel in the image, three values: one for red light, one for green light and one for blue light. Each of these values can be between 0 and 255; a pixel where all three values are 0 will be black and one where all three values are 255 will be white. By changing these values, it is possible for each pixel in the image to have one of 16,777,216 different colors.
The values for each light range from 0 to 255 because each is eight bits (or one byte). Thus, each pixel in a .bmp image has three bytes. Because it is a very "literal" format, practically describing the image to the computer, the .bmp format has wide compatibility: practically any system can play a .bmp image. The main advantage of BMP is this compatibility.
The problem is that it is very heavy. Imagine an image of 800 by 600 pixels; it will have 480 thousand pixels; if each pixel is 3 bytes long, the final image will be about 1.44 megabytes, which is too much space for an image of that size. And more: if the image is extremely simple, or a white rectangle, the file will still be huge.
2. JPG
First, the meaning: JPG is an abbreviation of the acronym JPEG, which stands for "Joint Photographic Experts Group", the name of an organization of photographers that created the format. It is one of the most widely used formats on the Internet, and the reason is simple: compared to .bmp, which was the most widely used format on the Internet at the time, it saves a lot of space.
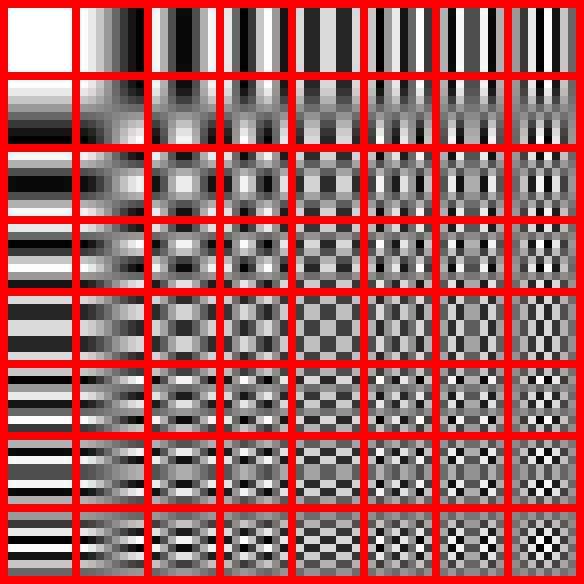
To do this, it divides the image into blocks of eight by eight pixels and for each of the 64 patterns represented in the image below. It then determines the "weight" of each of these patterns in each block.
The patterns in the lower right corner present very different pixels in a very small space. And our eyes usually can't even see these small differences. Therefore, depending on the pressure quality chosen by the user, either the standard blocks or this one is replaced by simpler blocks. This allows the final file to be much lighter, with very little loss of quality (at least as far as we can see with the naked eye).
The very small size is the main advantage of JPG files. The disadvantage is that the type of pressure it uses works best for still images. A .bmp photo has very few advantages over the same .jpg photo, but it is much heavier and, therefore, .jpg is more reassembled. But if you take graphic images, logos and company designs, you usually end up getting very noticeable distortions. See, for example, what happened to the star below:
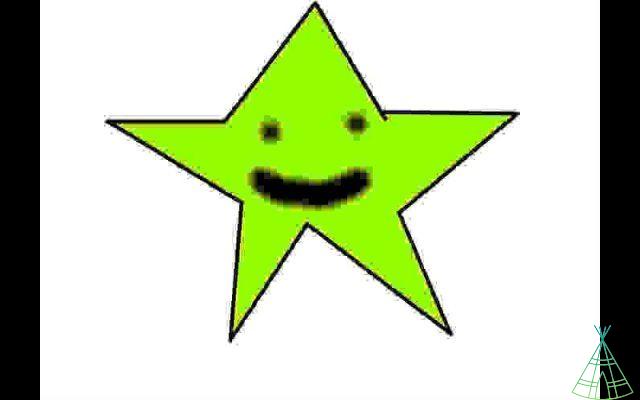
3. png
The acronym .png stands for "Portable Network Graphics" and, as its name suggests, was created to facilitate the exchange of images over the Internet. Like .jpg, this format uses pressure to reduce the weight of the files; however, unlike .jpg, the type of pressure used by .png does not involve as much loss of quality, especially in the case of graphic files.
See, for example, the benefits that the .png format brings to that poor star from above:
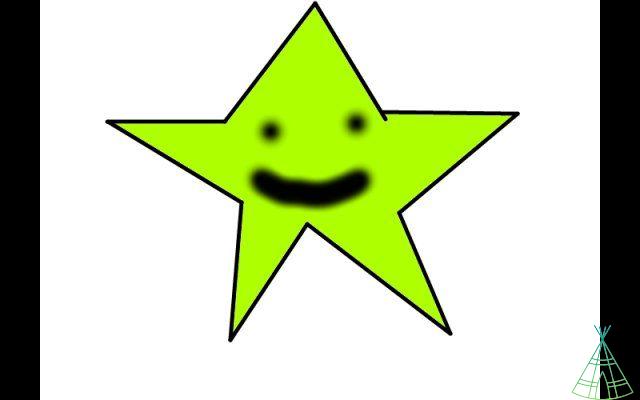

Naturally, the pressure is not as damaging, the final image ends up being heavier than if it were in .jpg format, but it is still lighter than a .bmp, for example. a mix of images in .png and .jpg, can, for example, make a site much clearer without any noticeable loss of quality.
But the main advantage of .png images is that the file also supports transparency. Transparency is usually indicated, in image editors, as a square. Anything that is squared in the editor will appear transparent in the file, meaning that it will have the background color of the website or image. It is easy to see that this feature makes the .png format very interesting for web designers.
So .png files have two advantages: the good balance between weight and quality, on the one hand, and support for transparencies, on the other. But that first point can also end up being a weakness: if the image requires a lot of quality, it might be better to use another format, and if it needs to be light, it might be better to use .jpg. It is worth bearing this in mind.
4. GIF
A feature of GIFs that I'm sure you already know: they can have several animated frames, which allows them to function as small, light, repetitive videos. This feature has made the .gif format one of the most beloved formats in the post-broadband Internet era (before broadband, many GIF websites were too heavy). It's hard to argue against the possibilities this presents:


But animation is just one of the features of GIFs. The acronym stands for "Graphics Interchange Format." The format came before .png and was intended precisely to overcome the pressure deficiency of .jpg for graphic files. It also uses pressure, but in a way that is optimized for graphics, logos and drawings.
As it turns out, because it is aimed at these types of images, it has some limitations when it comes to displaying videos or photos of real things. The most notable of these is that GIFs only support a maximum of 256 colors, which is sufficient for graphics but not enough for videos and photos. This limitation is the reason why dotted and oddly colored GIFs appear from time to time. Notice, for example, how the grass is grainy in the following GIF:
For this reason, a new format called APNG (or "animated PNG") has become popular. It does away with this color limitation and even adds support for transparencies. Apple started using it in iMessage iOS 10, and Google recently made Chrome compatible with this format. But the reign of the GIF format is likely to remain for some time.